Dubai
English
Request a call
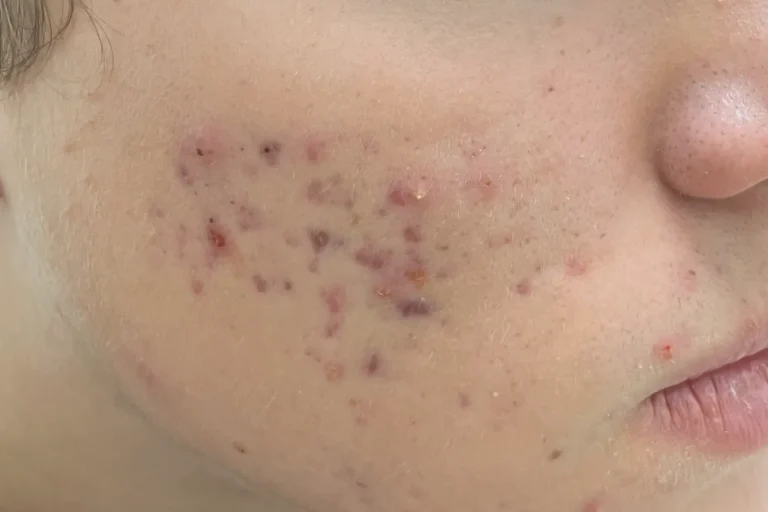
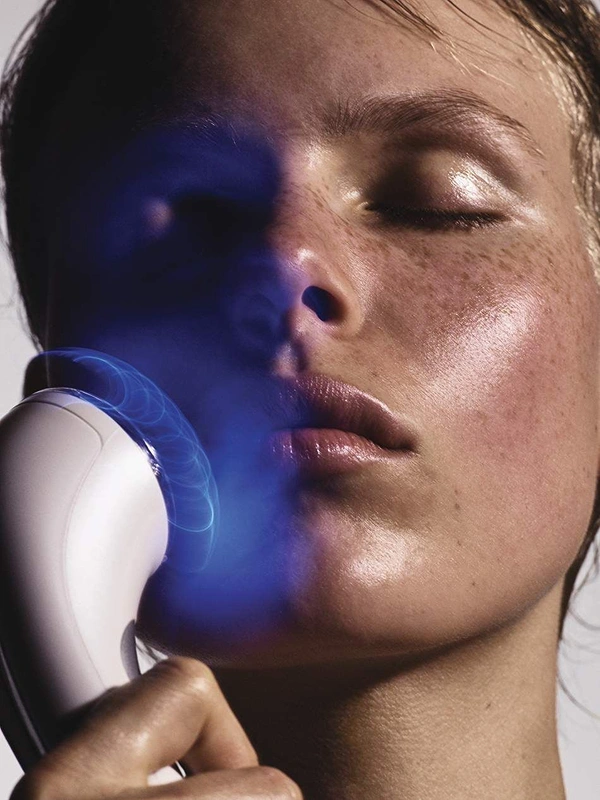
The question of what acne on the face is concerns not only teenagers. Adults also face this problem – regardless of gender, lifestyle, or age. Despite numerous “internet tips” and dozens of popular remedies, it’s important to understand: we are not just talking about pimples, but about a chronic skin condition. To effectively fight it, you need to understand where the inflammation comes from and why it shouldn’t be ignored.
What is acne? A simple answer to a complex question
If we try to simplify the medical definition, acne is an inflammatory skin disease in which the sebaceous glands become clogged with excess sebum and dead skin cells. This leads to comedones, papules, pustules, or more complex formations such as cysts: all of these appear as painful redness, bumps, or abscesses. The causes that provoke acne are varied:- Hormonal imbalances: during adolescence, pregnancy, menopause, or menstrual cycle disruptions.
- Genetics: the tendency to break out is often inherited.
- Stress: increases sebum production and triggers inflammation.
- Poor diet: excess sugar, dairy, fatty and processed foods.
- Improper skincare: harsh products, over-drying, lack of hydration.
- External factors: polluted air, tight clothing, touching the face with hands.
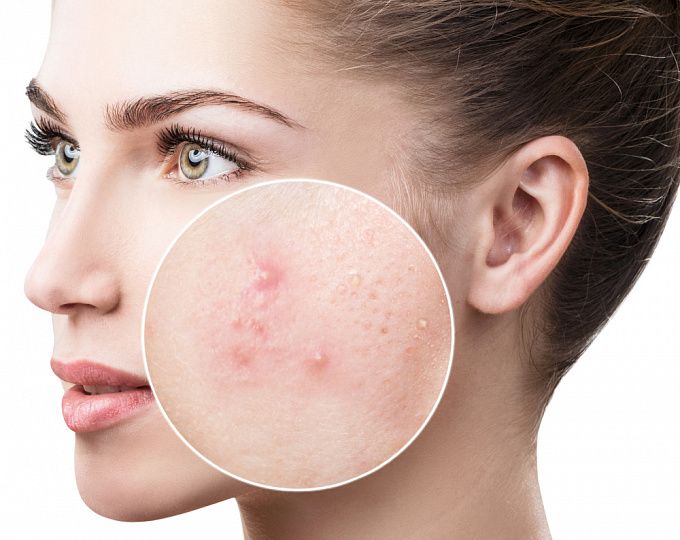
What Is Acne on the Skin: Not Just the Face
Acne on the skin is not always limited to the face. Breakouts can also appear on the body: back, shoulders, chest. In these areas, pores are also prone to clogging, especially with excessive sweating, friction from clothing, or the use of unsuitable skincare products. Skin changes on the body can be more painful and take longer to heal, as the skin here is thicker and harder to reach, so treating such inflammation requires special attention and consistency.Acne: What It Is and Why You Shouldn’t Ignore the Problem
Acne is not just a cosmetic issue but a sign of internal disruptions in the body. With acne, the body signals imbalances, and simply masking pimples with cosmetics doesn't solve the problem. Moreover, advanced inflammatory conditions can leave scars, enlarged pores, and persistent dark spots. Early consultation with a dermatologist not only shortens the treatment period but also helps prevent complications. The key is not to delay or self-medicate, especially in the case of frequent breakouts.What Is Skin Acne: Dependence on Skin Type
Many people don’t fully understand what skin acne is and confuse the terminology. Meanwhile, the type of epidermis directly affects the tendency toward inflammation:- Oily and combination skin is most often prone to clogged pores and breakouts in the T-zone.
- Dry skin is less susceptible, but localized acne can still appear when the skin is overly dried out.
- Sensitive skin can react with irritation even to skincare products, provoking breakouts and flaking.
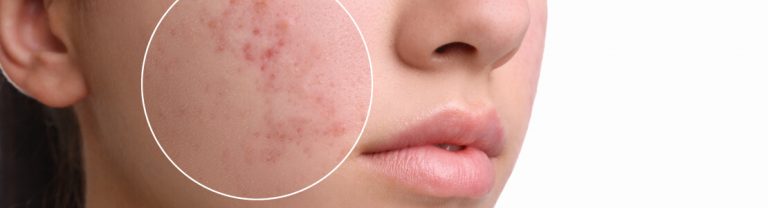
Pimple or Condition: How to Tell the Difference
When encountering a single pustule, people often wonder: is it just irritation or the beginning of acne? A solitary pimple can result from diet, friction, or a reaction to skincare products. But if inflammations appear regularly and are accompanied by oily shine, enlarged pores, and clogged follicles — it's most likely a skin condition. In such cases, it's important not to delay a visit to the doctor. A dermatologist will conduct a diagnosis and develop a treatment plan based on the cause of the skin imbalance.Typical Areas of Inflammation on the Face and Body
To better understand how inflammations form, it's important to know where they most commonly occur:- Forehead and nose – areas with high sebaceous gland activity, often develop blackheads and small breakouts.
- Chin – reacts to hormonal changes and diet, especially sweets and dairy products.
- Cheeks – suffer from constant contact with gadgets and hands, often inflame in those who use their phone without disinfecting it.
- Back and shoulders – sensitive to friction, sweating, and synthetic fabrics, especially in summer.
- Décolleté area – may become inflamed due to improper care, excessive perfume, and tight clothing.
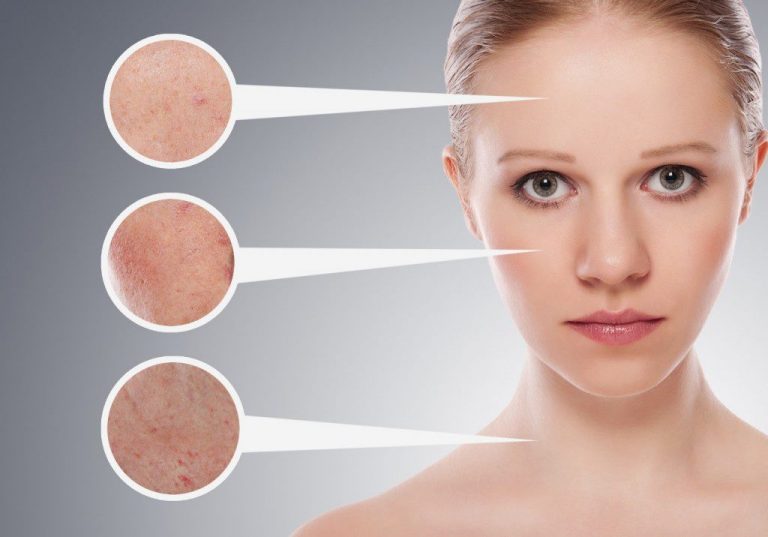
How to Help Your Skin: Simple but Important Steps
Although treatment is individual, there are universal tips that help reduce inflammation and improve skin condition:- cleanse your skin twice a day with gentle, alcohol-free products — this helps maintain balance without over-drying;
- use pharmacy skincare with salicylic, azelaic, or glycolic acid – they reduce inflammation and clear pores;
- limit consumption of sugar, fatty, and dairy foods – these products can trigger breakouts;
- avoid popping pimples – this causes new inflammation and increases the risk of scarring and spots;
- manage stress – chronic tension worsens breakouts through hormonal imbalance;
- maintain regular sleep and hygiene (changing pillowcases, wiping your phone) – this helps reduce the number of microbes on the skin.
Acne Is Not Forever
Acne is a solvable problem with a comprehensive approach: skincare, medical examination, working on psychological well-being, and, if needed, treatment under a doctor’s supervision. Don’t ignore the symptoms or wait for them to go away on their own. The earlier the therapy starts, the fewer marks will remain on your skin and self-esteem. Let the journey to clear skin be conscious, consistent, and gentle – and the result will surely please you. Our website features the following popular types of services:
Fill out the form to book your consultation.
Your personal manager will contact you within 10 minutes and arrange a convenient time for your visit.