Dubai
English
Request a call
What is a protein diet

A protein diet is a way of eating that involves consuming foods rich in proteins while limiting the intake of carbohydrates and fats. This is a modification of easily digestible nutrition. This option should not be followed independently, for example, under the influence of an emotional decision. It is necessary to consult a doctor and a nutritionist beforehand. What can be eaten on a protein diet and what can be avoided is described below. The goal of this type of nutrition is to provide the body with the necessary amount of protein required for building and restoring cells, maintaining immunity, and producing hormones and enzymes. The method requires proper balance and health monitoring.

What does a protein diet provide and who is it suitable for
Proteins (also called proteins) are high-molecular compounds that perform extremely important functions in the body. What does this give the body? Among other things, they are responsible for providing energy, maintaining proper brain function, appropriate blood pressure, water balance, and supporting numerous metabolic processes. Proteins obtained from food are broken down by proteolytic enzymes into amino acids, which can be used for the synthesis of the body's own proteins. The substances are divided into:- animal – highly nutritious, complete;
- plant-based, characterized by lower nutritional value.
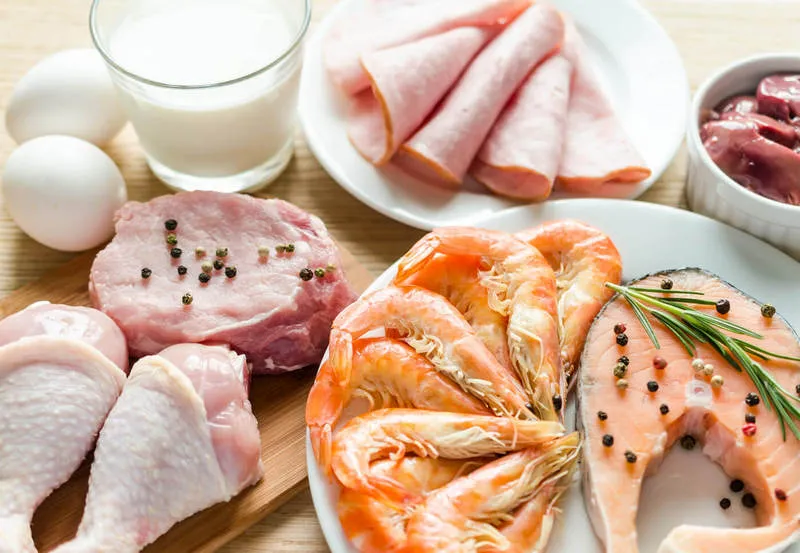

What is included in a protein diet? The selection of a diet depends on many factors, including age, sex, body weight, physiological condition, and energy expenditure associated, for example, with physical activity. It is assumed that for the proper functioning of the body, one should consume at least 0.8 g of protein per 1 kg of body weight per day. A slightly higher demand is observed in children, adolescents, pregnant and breastfeeding women.
The method is mainly recommended for people:
- with chronic fatigue;
- during recovery after illness (for example, after a stroke, surgery, extensive burns, or body injuries);
- with a diagnosis of hepatitis or hyperthyroidism.
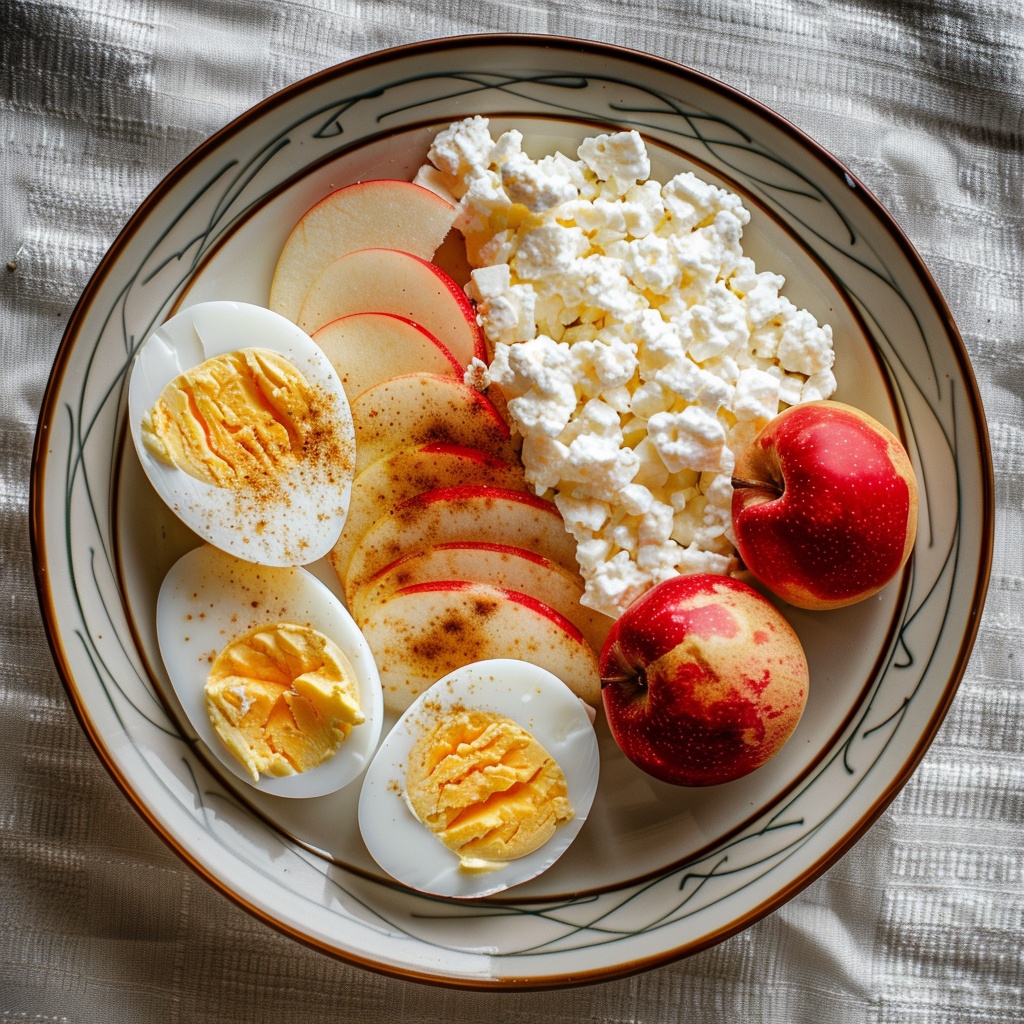

Protein diet – what can be eaten in this situation
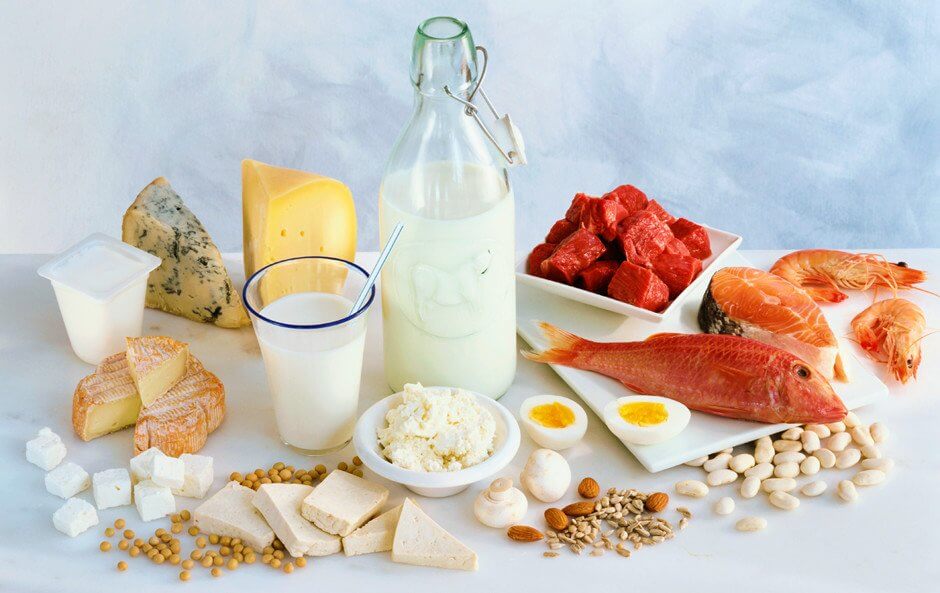
In such a diet, 2/3 of the protein should come from animal products – they are easier to digest, better absorbed, and contain a complete set of dietary amino acids, including the so-called exogenous ones, i.e., those that are not synthesized by the human body. The source should be lean meat, fish, eggs, and dairy products. Protein food – what it means in terms of the menu:- Cereal products – wheat bread (crispbreads, rolls), yeast bread, rusks, finely and medium-grained cereals, white rice.
- Milk and dairy products – skimmed or semi-skimmed options, cottage cheese, unsweetened natural drinks.
- Lean fish – cod, perch, trout, perch, pike-perch, tench. Less often – mackerel, hake, sardine, herring.
- What the diet includes from meat – lean veal, rabbit, turkey, and chicken without skin. Less often: beef, lean pork.
- Fats – butter or oil. Exceptions are palm and coconut oil.
- Vegetables – carrot, zucchini, pumpkin, tomatoes, potato, spinach, parsley, beetroot, kohlrabi, green beans, lettuce. Less often – broccoli, cauliflower, green peas, rhubarb, spinach, green beans, cabbage.
- What fruits can be consumed – berries (blueberry, strawberry, raspberry, blackberry, wild strawberry), citrus fruits, baked or boiled apples, bananas. Less often – melon, cherry, kiwi, plum.
- Ground sunflower, flax, sesame seeds.
- Eggs – soft-boiled, fried eggs, steamed omelet.

Protein diet – what you can eat and what is better to avoid
Every type of proper nutrition necessarily includes contraindications. What should be avoided in this case:- cereal products – wholemeal bread or bread with added sugar, cornflakes, coarse grains;
- milk and dairy products – fatty cottage cheese, condensed milk, sweetened yogurts, aged fatty cheeses, cream;
- meat – fatty pork, lamb, duck, lard, sausages, wieners, pâtés, canned meat;
- fish – halibut, bream, eel;
- fats – clarified butter, cooking fat for frying;
- which vegetables are not recommended – garlic, onion, cucumbers, leek, pepper, turnip, dried legumes, radish;
- fruits – pears, dates, fruits in sugar syrups, candied fruits, dried fruits;
- spices – pepper, mustard, curry, nutmeg, bouillon cubes, ketchup, soy sauce;
- eggs hard-boiled, fried in fat;
- cakes, pastries, bars.
Fill out the form to book your consultation.
Your personal manager will contact you within 10 minutes and arrange a convenient time for your visit.